HaF is a reward model training framework for high-quality alignment.
The reward model has become increasingly important in alignment, assessment, and data construction for large language models (LLMs). Most existing researchers focus on enhancing reward models through data improvements, following the conventional training framework for reward models that directly optimizes the predicted rewards.
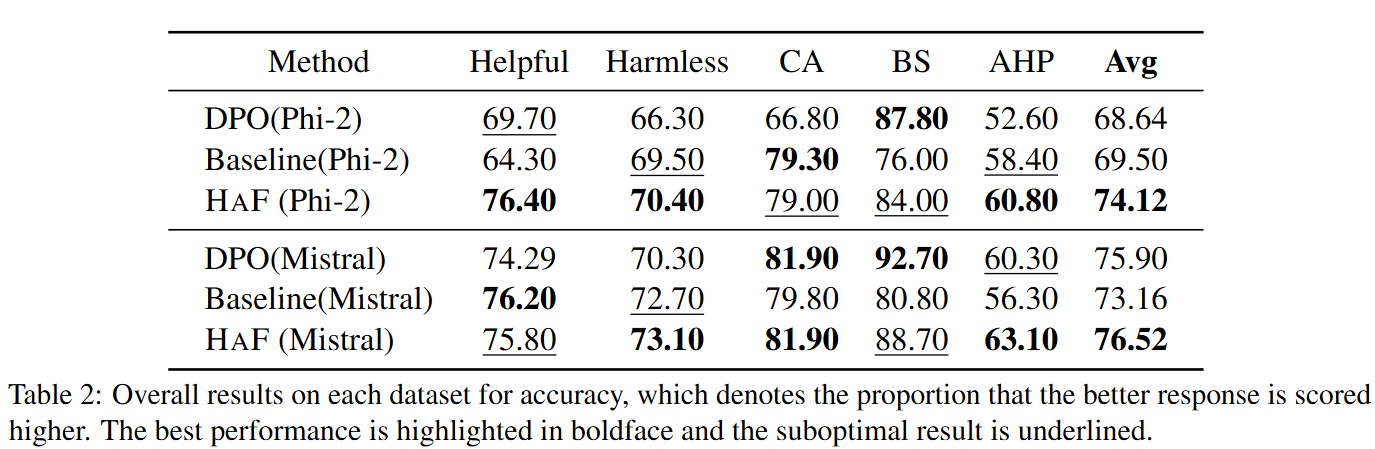
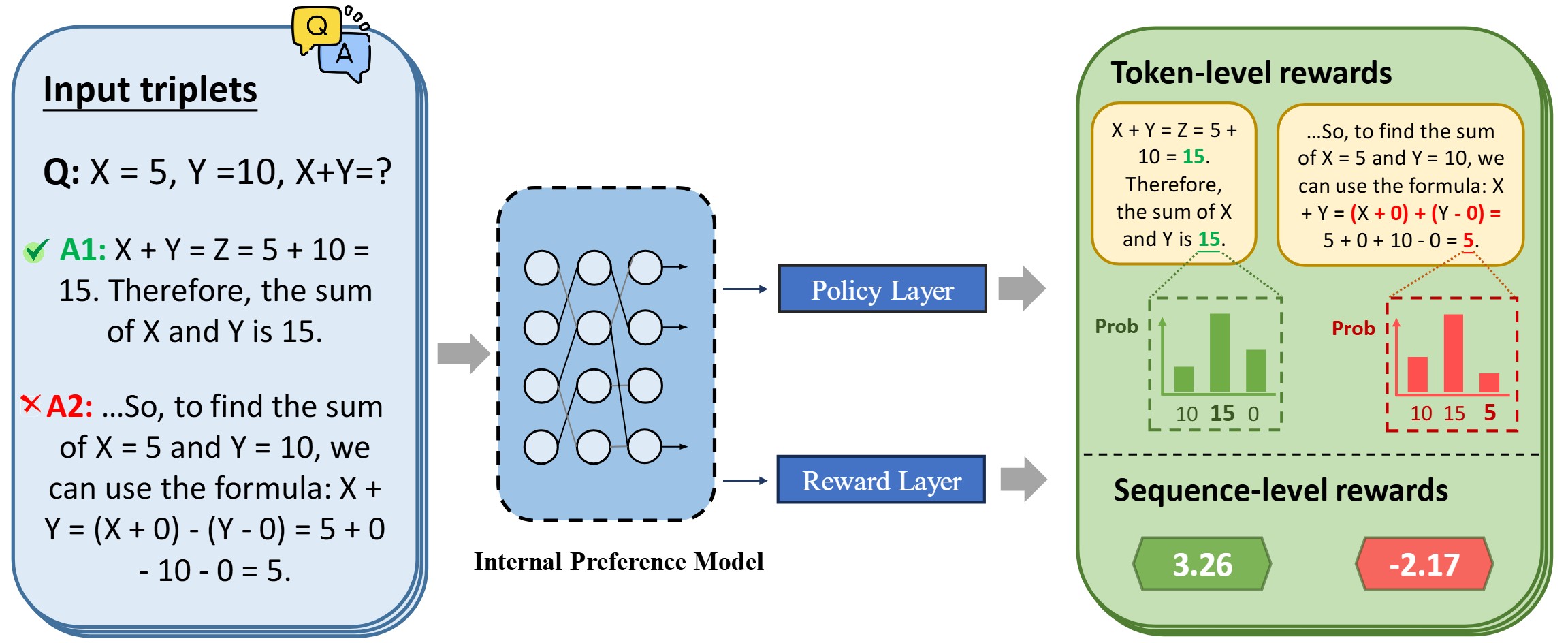
In this paper, we propose a hybrid alignment framework HaF-RM for reward model training by introducing an additional constraint on token-level policy probabilities in addition to the reward score. It can simultaneously supervise the internal preference model at the token level and optimize the mapping layer of the reward model at the sequence level.
Theoretical justifications and experiment results on five datasets show the validity and effectiveness of our proposed hybrid framework for training a high-quality reward model. By decoupling the reward modeling procedure and incorporating hybrid supervision, our HaF-RM framework offers a principled and effective approach to enhancing the performance and alignment of reward models, a critical component in the responsible development of powerful language models.
Training the reward model involves aligning the model preference and learning a "preference-reward" projection. Initialized with well-trained LLM, the reward model has nearly aligned preference while it has to learn the projection from scratch.
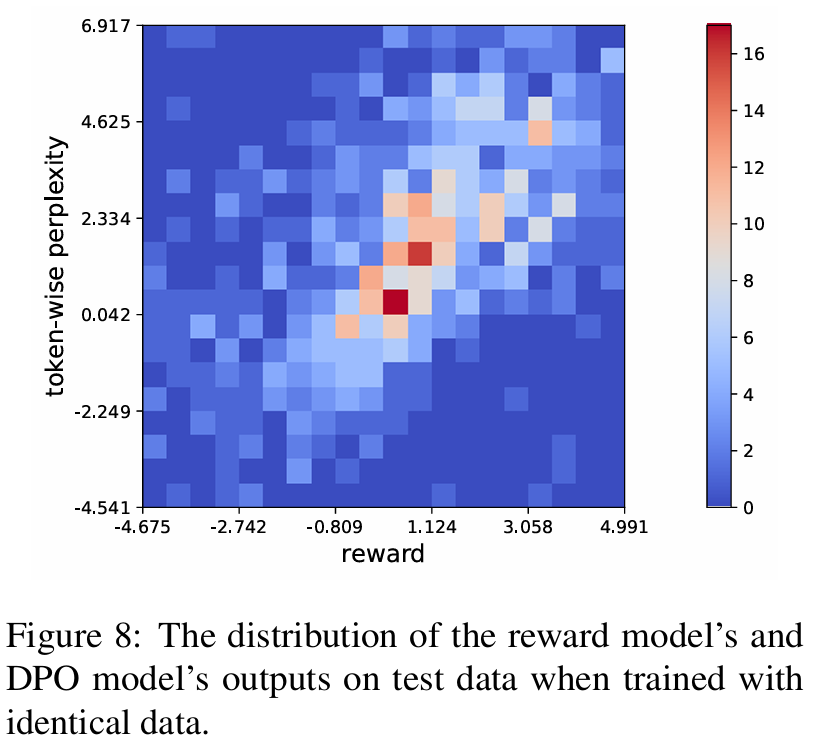
DPO loss shares the same premise with reward loss. DPO model can be considered as a token-wise reward model which functions similarly with the standard reward model (sequence-wise). So we can use DPO loss as an auxiliary loss function to improve the stability of training process and further boost the reward model's performance.


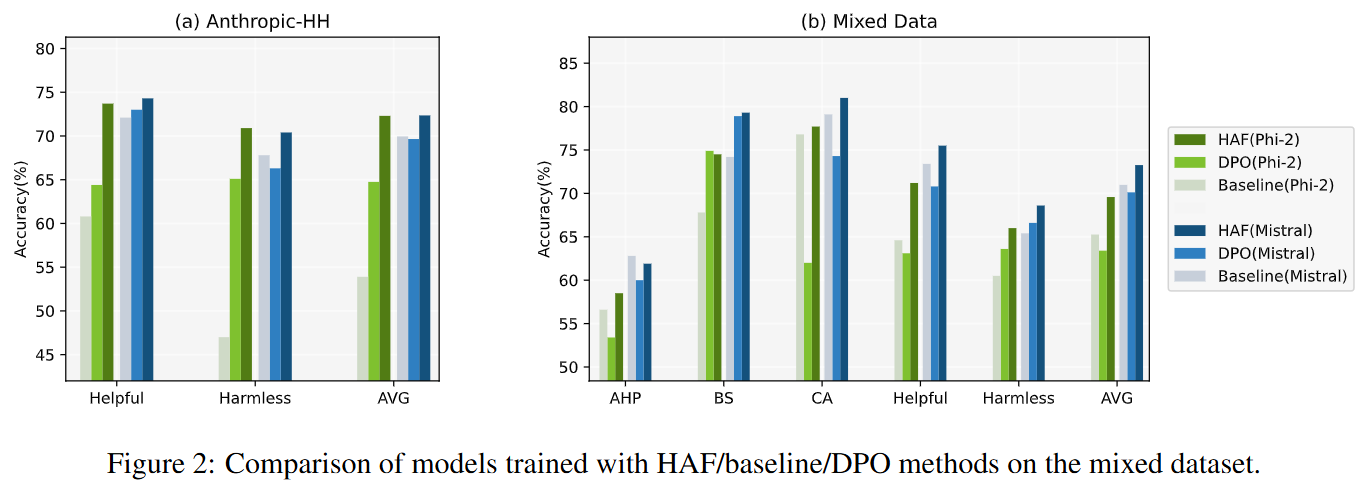
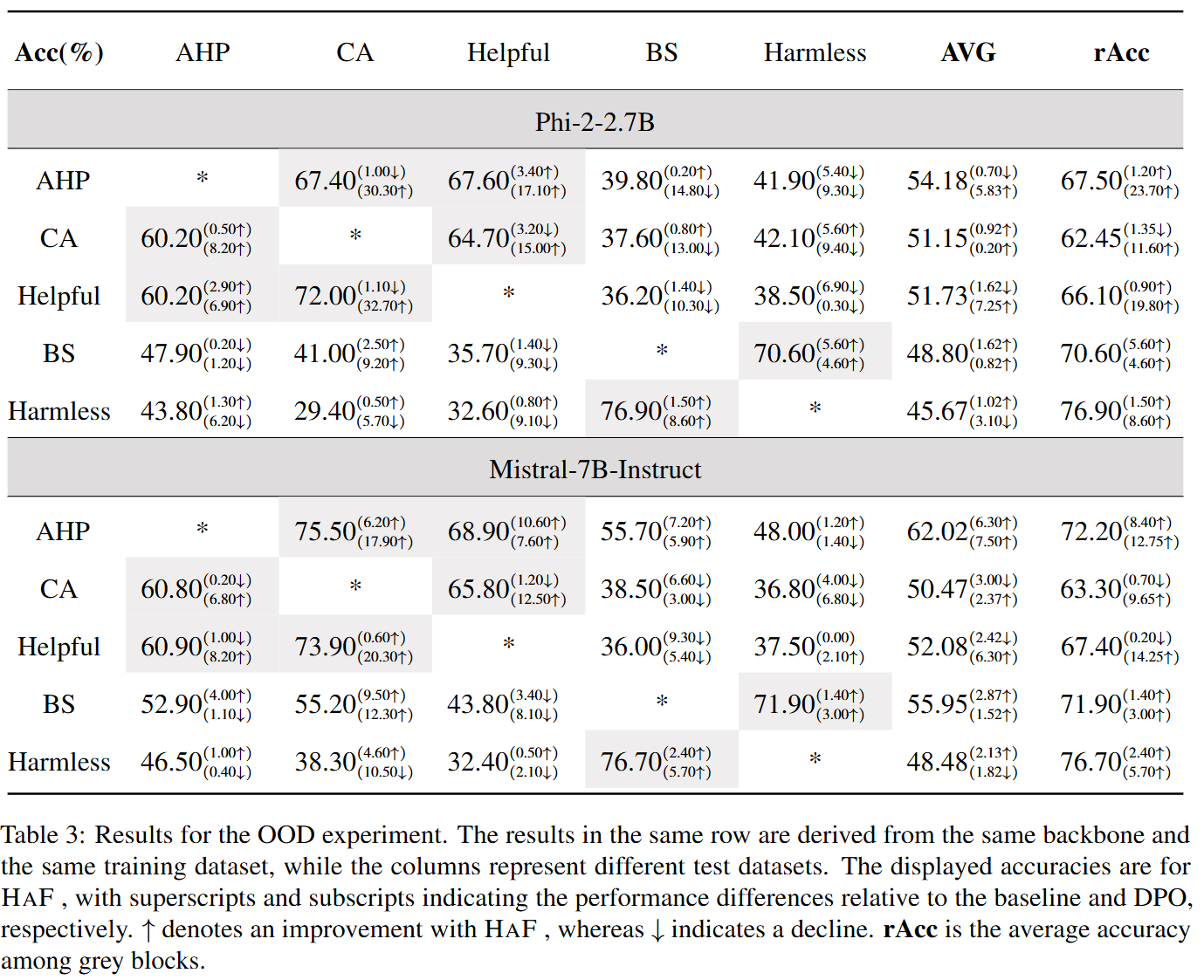
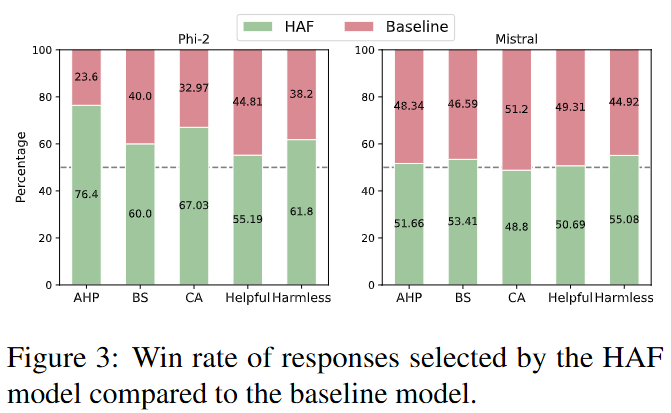
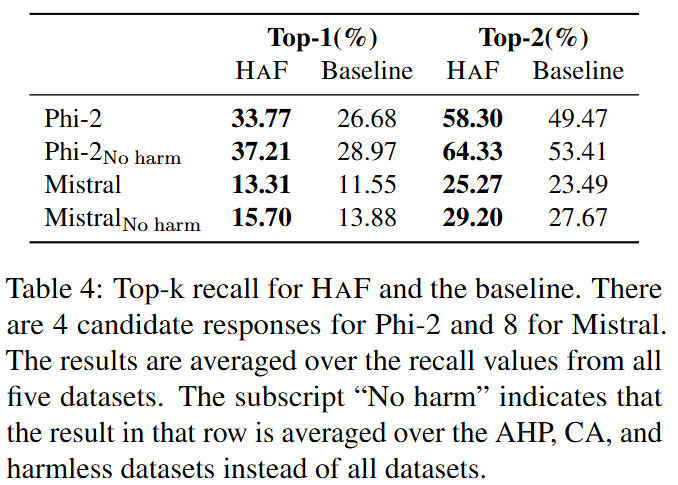
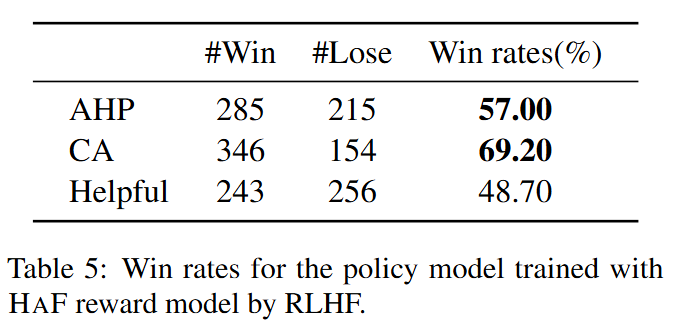
The model trained with HaF has higher win rates.
@article{liu2024hafrm,
title={HaF-RM: A Hybrid Alignment Framework for Reward Model Training},
author={Liu, Shujun and Shen, Xiaoyu and Lai, Yuhang and Wang, Siyuan and Yue, Shengbin and Huang, Zengfeng and Huang, Xuanjing and Wei, Zhongyu},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2407.04185},
year={2024}
}